摘要
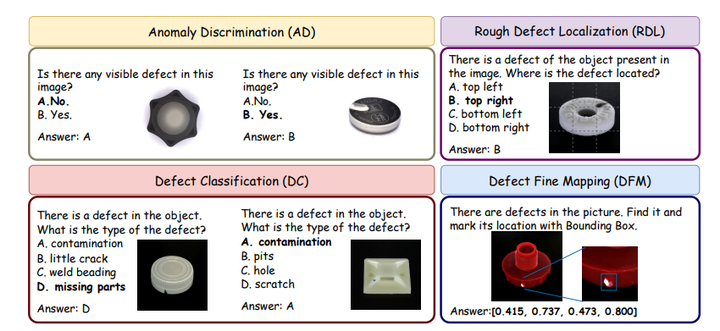
Industrial Anomaly Detection (IAD) is critical to ensure product quality during manufacturing. Although existing zero-shot defect segmentation and detection methods have shown effectiveness, they cannot provide detailed descriptions of the defects. Furthermore, the application of large multimodal models in IAD remains in its infancy, facing challenges in balancing question-answering (QA) performance and maskbased grounding capabilities, often owing to overfftting during the ffne-tuning process. To address these challenges, we propose a novel approach that introduces a dedicated multi-modal defect localization module to decouple the dialog functionality from the core feature extraction. This decoupling is achieved through independent optimization objectives and tailored learning strategies. Additionally, we contribute to the ffrst multimodal industrial anomaly detection training dataset, named Defect Detection Question Answering (DDQA), encompassing a wide range of defect types and industrial scenarios. Unlike conventional datasets that rely on GPT-generated data, DDQA ensures authenticity and reliability and offers a robust foundation for model training. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed method, Explainable Industrial Anomaly Detection Assistant (EIAD), achieves outstanding performance in defect detection and localization tasks. It not only signiffcantly enhances accuracy but also improves interpretability. These advancements highlight the potential of EIAD for practical applications in industrial settings. Code and datasets will be available at https://github.com/Solunny/EIAD.